Schedule Appointment

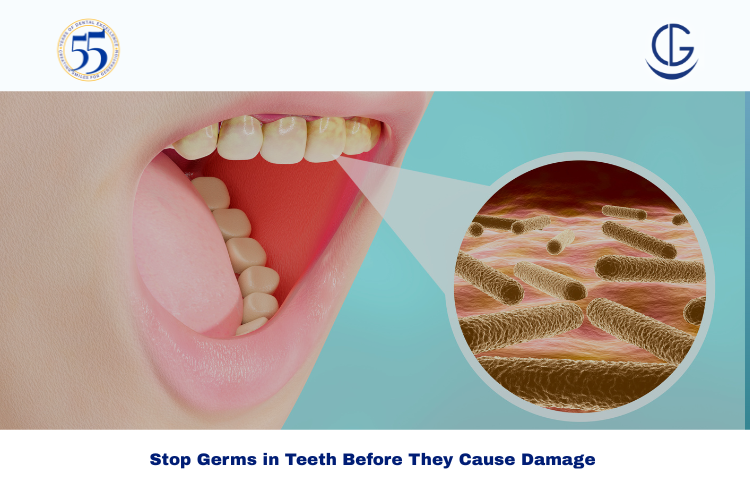
If you’ve ever had a toothache that just won’t go away, you might be dealing with more than just a bit of discomfort — germs in teeth could be the culprit. At Dr Gowds Dental Hospital in Hyderabad, we often see patients who delay treatment because they don’t recognize the early warning signs of bacterial infections in the mouth. Ignoring these signs can lead to serious oral health problems, including gum disease, tooth decay, and even infections that spread to other parts of the body.
In this guide, we’ll break down how to spot these germs, what they do to your teeth, and practical home remedies to help manage them — plus when it’s time to call in the professionals.
Germs in teeth refer to bacteria that build up in the mouth, often due to poor oral hygiene, sugary diets, or untreated dental issues. These bacteria feed on food particles and release acids that erode tooth enamel, irritate gums, and sometimes cause painful infections.
Common harmful bacteria include Streptococcus mutans (responsible for cavities) and Porphyromonas gingivalis (linked to gum disease).
Identifying early symptoms can save you from more invasive dental procedures later. Watch out for:
These remedies can help reduce bacterial activity and manage symptoms until you visit a dentist. They are not substitutes for professional care.
Benefits: Saltwater is a natural disinfectant that reduces swelling and kills some bacteria.
How to Use: Mix ½ teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water. Swish for 30 seconds and spit out. Repeat 2–3 times daily.
Precautions: Avoid swallowing the rinse.
Benefits: Coconut oil has antibacterial properties that help remove germs in teeth and gums.
How to Use: Swish 1 tablespoon of coconut oil in your mouth for 10–15 minutes. Spit into a trash bin, not the sink, to prevent clogging pipes.
Precautions: Do not swallow the oil.
Benefits: Clove oil contains eugenol, which has antibacterial and pain-relieving properties.
How to Use: Dilute a few drops with carrier oil, apply to the affected area using a cotton swab.
Precautions: Use sparingly; too much can cause gum irritation.
Benefits: Helps kill bacteria, whiten teeth, and heal bleeding gums.
How to Use: Mix equal parts 3% hydrogen peroxide and water. Swish for 30 seconds.
Precautions: Do not swallow. Avoid using it daily for long periods.
Benefits: Rich in antioxidants that fight bacteria and reduce inflammation.
How to Use: Brew green tea, let it cool, and use it as a mouth rinse twice daily.
Precautions: Avoid sweetening the tea.
While home remedies can help in the short term, some cases require urgent care. Visit your dentist if you notice:
At Dr Gowds Dental Hospital, we provide advanced treatments for bacterial infections, from root canal therapy to gum disease management.
Teeth bacteria are definitely more than just an annoyance—they become the cause of infections if left untreated. Saltwater rinse, oil pulling, clove oil, hydrogen peroxide, and green tea are among the things that can act as antibacterials, however, they are not going to be enough and you will still need the dentist. When the symptoms remain or become more severe, an accurate diagnosis and treatment from the expert at Dr Gowds Dental Hospital in Hyderabad is necessary.
Basically, the germs in the teeth are caused by plaque, which results from poor oral hygiene, sugary diets, and no regular dental check-ups.
The answer is definitely no, as they only can decrease the bacteria for a short time, while only professional dental cleaning or treatment can completely eliminate the harmful bacteria.
Brushing the teeth twice and flossing once a day, having a well-balanced diet, and using antibacterial rinses will provoke the least bacterial buildup naturally.
If there are no signs of your pain going away and the swelling is still there, or if it looks infected in any way, then reach out to Dr Gowds Dental Hospital in Hyderabad right away. Your problem shall be solved with the help of expert dentists.
Obviously, the bacteria that are not treated can be the cause of cavities, gum disease, and even infections that may be spread beyond the mouth.